To maximise the safety of occupants by enabling them to be close enough to an exit to safely evacuate.
Travel distances
The D2D5 travel distances are based on an assumption of what is considered “reasonable” distances to be travelled by occupants in reaching an exit.
Method of measurement
The travel distances specified in D2D5 are measured in accordance with D2D20.
Class 2 and Class 3 buildings and Class 4 parts—D2D5(1) and (2)
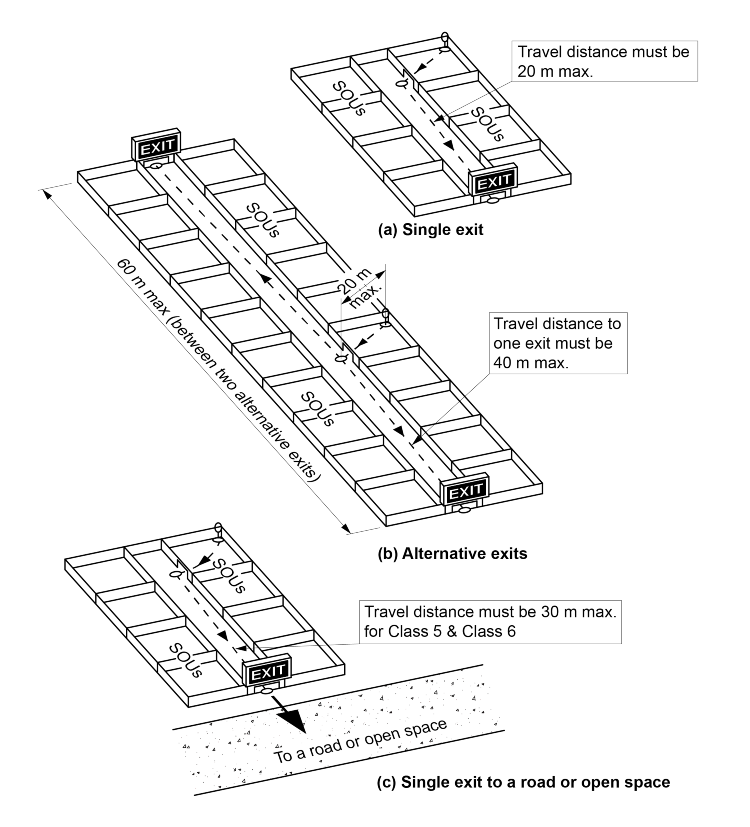
D2D5(1) and (2) require a shorter travel distance, to a single exit, for Class 2 and Class 3 buildings and Class 4 parts than is required for Class 5 to Class 9 buildings.
The distance occupants of sole-occupancy units in Class 2 and Class 3 buildings and Class 4 parts must travel to leave
their unit is not part of the distance specified in D2D5. Accordingly, the permitted distance of travel from the point at which the occupant leaves the unit must take account of the time needed for the occupant to reach that point from within the unit.
Distance of travel must factor in the time occupants need to wake up, become alert to their predicament, and exit in a state of confusion.
This process of becoming alert will inevitably require more time to exit. Therefore, the distance of travel to an exit should be shorter.
Figure D2D5a illustrates various methods of complying with D2D5 for Class 2 and Class 3 buildings and Class 4 parts of buildings.
Class 5 to Class 9 buildings—D2D5(3)(a)
D2D5(3)(a) sets out the maximum travel distance in Class 5–9 buildings. This includes Class 9c buildings, but excludes Class 9a buildings, which must comply with D2D5(4). (See comments on D2D5(4) for the reason Class 9a buildings are treated differently). The additional travel distance allowed in Class 9c buildings recognises the effectiveness of sprinkler systems that must be installed in these buildings.
The distances specified allow people to evacuate in a reasonable time, assuming that they are not asleep.
In case a fire blocks a path of travel, D2D5(3)(a) requires that alternative routes must be available within 20 metres of the starting point, unless it is possible to reach a single exit within 20 m.
The conditional reference in D2D5(3) to sub-clauses (4), (5) and (6) refers to special provisions for particular types of buildings.
Figure D2D5b illustrates various methods of complying with D2D5 for Class 5 to 9 buildings.
Class 5 and Class 6 buildings—D2D5(3)(b)
D2D5(3)(b) provides a concession for Class 5 and Class 6 buildings served by a single exit opening onto a road or open space. The concession only applies to the storey at the level of access to a road or open space.
D2D5(3)(b) uses the phrase “at the level of access to a road or open space”. The term “level” does not require the storey to be physically level or flush with the road or open space to obtain the concession, but simply requires that the storey is at a level from which occupants finally leave the building to reach a road or open space. The concession allows a greater travel distance of 30 m in lieu of 20 m to a single exit on the basis that occupants, including customers of a shop, are:
- generally aware of their surroundings in these types of buildings which are typically small shops or offices located at or near ground level;
- familiar with the location of the exit which is typically the main entrance to the shop or office; and
- familiar with the path of travel to reach the exit thereby allowing a prompt and direct egress from the space.
Small shops and offices at or near ground level also tend to have an open plan layout thereby allowing the exit to be easily sighted to permit safe and speedy egress where the space is located in close proximity to the external ground surface such as a road or open space.
The concession is applicable to a number of cases such as to any Class 5 and 6 parts of a building located in a storey at the level of access to a road or open space even though the storey may be served by more than one exit, subject to that part otherwise complying with D2D5(3)(b).
The concession is also available for Class 5 or 6 parts of a building containing other classifications (refer to A1G1(3)(a)).
The conditional reference in D2D5(3) to sub-clauses (4), (5) and (6) refers to special provisions for particular types of building.
Patient care areas—D2D5(4)
Patient care areas in Class 9a buildings can present particular problems in case of emergency egress. Such areas are likely to be occupied by people who are either fully or partly non-ambulatory, and in many cases confused or incapacitated by drugs and medical and post-operative conditions.
Accordingly, the allowable distance of travel to an exit in the patient care areas of a Class 9a building is less than for Class 5–8 buildings, non-patient care areas of Class 9a buildings, and Class 9b buildings.
D2D5(4) should be read in conjunction with C3D6.
Open spectator stands—D2D5(5)
The construction of an open spectator stand is such that the build up of smoke is unlikely. Greater distances of travel to an exit are therefore permitted.
Assembly buildings—D2D5(6)
The concession available for assembly buildings is based on a specific level of fire and smoke separation being provided between the area being evacuated and the circulation space passed through to reach an exit.
To obtain the concession, D2D5(6)(c) limits the distance of travel through the room being evacuated and across the circulation space outside that room to the exit.
Figure D2D5a: Distances to exits in Class 2 and Class 3 buildings
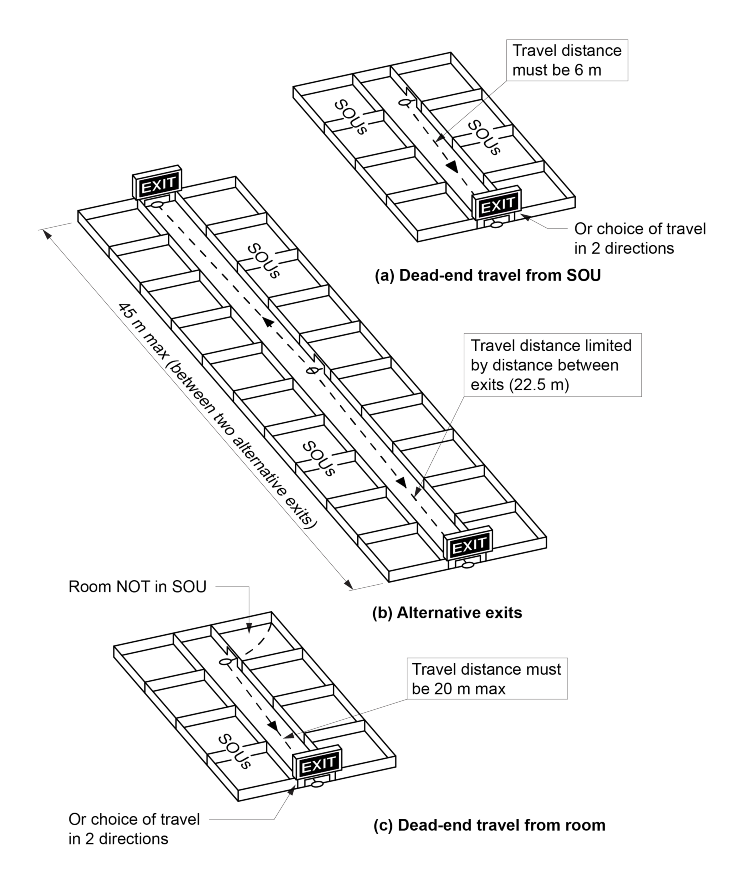
Figure D2D5b: Distance to exits in Class 5 to Class 9 buildings